Optical Probe Development
Optical Probe Development
Optical probe design
Specialized software and manufacturing processes allow our lab to design custom optical systems, including imaging lenses, lens assemblies, and optical probes. For the purpose of imaging biological systems in vivo, we design rigid endoscopic probes based off the use of gradient index (GRIN) lenses with diameters down to 0.350 mm. Where access to tissues is restricted by organ curvature, we also design flexible endoscopic probes based on coherent fiber bundles. Together, these allow the clear imaging of a wide variety of organs and tissues.
Optical probe design
Specialized software and manufacturing processes allow our lab to design custom optical systems, including imaging lenses, lens assemblies, and optical probes. For the purpose of imaging biological systems in vivo, we design rigid endoscopic probes based off the use of gradient index (GRIN) lenses with diameters down to 0.350 mm. Where access to tissues is restricted by organ curvature, we also design flexible endoscopic probes based on coherent fiber bundles. Together, these allow the clear imaging of a wide variety of organs and tissues.
Side-view and catadioptric endoscope probes
Endoscopic probes are commonly used to observe the surfaces of organs, but several tissues of interest such as the colon and esophagus are best viewed in a direction perpendicular to the direction from which the probe must enter. Side-view and catadioptric endoscope probes, which incorporate mirrors to redirect the imaging path, allow the user to better view into pores and crevases of the epithelium. Side-view probes have been shown to improve diagnosis for colon cancer.

Side-view and catadioptric endoscope probes
Endoscopic probes are commonly used to observe the surfaces of organs, but several tissues of interest such as the colon and esophagus are best viewed in a direction perpendicular to the direction from which the probe must enter. Side-view and catadioptric endoscope probes, which incorporate mirrors to redirect the imaging path, allow the user to better view into pores and crevases of the epithelium. Side-view probes have been shown to improve diagnosis for colon cancer.
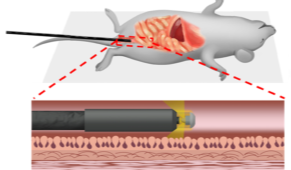
Needle-injection endoscopes and needle probes
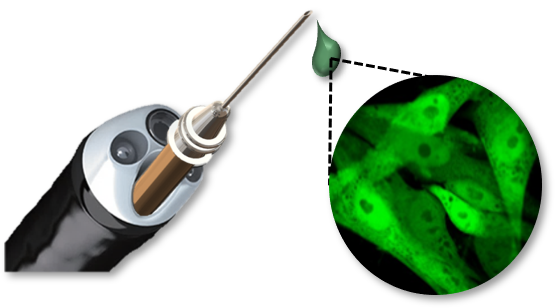
Endoscopic probes which incorporate fine needles allow the delivery of trace amounts of pharmaseuticals or cells directly to epithelial tissues. This is useful for the targeting of stem cell therapy and photodynamic therapy. It also is ideal for the modelling of cancers: cancer cells can be injected into experimental animals to form tumors where naturally-occurring cancers commonly appear.
Endoscopic probes can also be incorporated into needles, allowing the probe to examine parts of the body which are not otherwise accessible.

Needle-injection endoscopes and needle probes
Endoscopic probes which incorporate fine needles allow the delivery of trace amounts of pharmaseuticals or cells directly to epithelial tissues. This is useful for the targeting of stem cell therapy and photodynamic therapy. It also is ideal for the modelling of cancers: cancer cells can be injected into experimental animals to form tumors where naturally-occurring cancers commonly appear.
Endoscopic probes can also be incorporated into needles, allowing the probe to examine parts of the body which are not otherwise accessible.
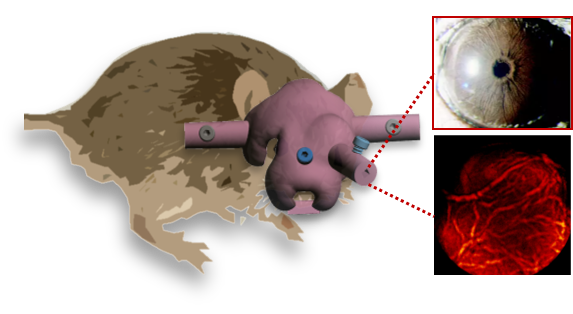
Image stabilization utilizing probe
Light can be used to selectively kill cancer cells with the application of photosensitizing compounds, which emit cancer-killing reactive oxygen species upon illumation. Our laboratory is pursuing several aspects of this therapy, from the illuminator design to the localized application of photosensizer via endoscopy.

Image stabilization utilizing probe
Light can be used to selectively kill cancer cells with the application of photosensitizing compounds, which emit cancer-killing reactive oxygen species upon illumation. Our laboratory is pursuing several aspects of this therapy, from the illuminator design to the localized application of photosensizer via endoscopy.
* Selected papers:
- “Stereotaxic endoscopy for the ocular imaging of awake, freely-moving animal models”, Journal of Biophotonics, Vol 13(5), e201960188, May, 2020. (Featured article as the Journal Cover)
- “Longitudinal micro-endoscopic monitoring of high-success intramucosal xenografts for mouse models of colorectal cancer,” International Journal of Medical Sciences (IJMS), Vol 16(11), 1453-1460, Sep. 2019. (Featured as the Journal Cover)
- “Miniaturized omnidirectional flexible sideview endoscope for rapid monitoring of thin tubular biostructures,” Biomedical Optics Express, Vol 10 (5), 2264-2274, April 2019.
- “Longitudinal Tracing of Spontaneous Regression and Anti-angiogenic Response in Individual Microadenomas during Colon Tumorigenesis,” Theranostics, Vol. 5, No.7, pp. 724-732, April 2015. (Featured as the Journal Cover)
- “Optical fine-needle imaging biopsy of the brain,” Biomedical Optics Express, Vol.4, No.12, pp. 2846-2854, Dec. 2013.
- “350-um side-view optical probe for imaging the murine brain in vivo from the cortex to the hypothalamus,” Journal of Biomedical optics, Vol. 18, No. 5, 050502, May 2013.
- “Endoscopic time-lapse imaging of immune cells in infarcted mouse hearts,” Circulation Research, Vol. 112, No.6, pp.891-899, Mar. 2013.
- “Fabrication and operation of GRIN probes for in vivo fluorescence cellular imaging of internal organs in small animals,” Nature Protocols, Vol.7, No.8, pp.1456-1469, Aug. 2012. (Featured as the Journal Cover)
- “In vivo imaging of tracheal epithelial cells in mice during airway regeneration,” American Journal of Respiratory Cell and Molecular Biology(AJRCMB), Vol. 47, No.6, pp.864-868, Dec. 2012. (Most-read Article during Oct. 2012)

Cover article of
Journal of Biophotonics
Cover article of
Theranostics
Cover article of
Int. J. Med. Sci
* Selected papers:
- “Stereotaxic endoscopy for the ocular imaging of awake, freely-moving animal models”, Journal of Biophotonics, Vol 13(5), e201960188, May, 2020. (Featured article as the Journal Cover)
- “Longitudinal micro-endoscopic monitoring of high-success intramucosal xenografts for mouse models of colorectal cancer,” International Journal of Medical Sciences (IJMS), Vol 16(11), 1453-1460, Sep. 2019. (Featured as the Journal Cover)
- “Miniaturized omnidirectional flexible sideview endoscope for rapid monitoring of thin tubular biostructures,” Biomedical Optics Express, Vol 10 (5), 2264-2274, April 2019.
- “Longitudinal Tracing of Spontaneous Regression and Anti-angiogenic Response in Individual Microadenomas during Colon Tumorigenesis,” Theranostics, Vol. 5, No.7, pp. 724-732, April 2015. (Featured as the Journal Cover)
- “Optical fine-needle imaging biopsy of the brain,” Biomedical Optics Express, Vol.4, No.12, pp. 2846-2854, Dec. 2013.
- “350-um side-view optical probe for imaging the murine brain in vivo from the cortex to the hypothalamus,” Journal of Biomedical optics, Vol. 18, No. 5, 050502, May 2013.
- “Endoscopic time-lapse imaging of immune cells in infarcted mouse hearts,” Circulation Research, Vol. 112, No.6, pp.891-899, Mar. 2013.
- “Fabrication and operation of GRIN probes for in vivo fluorescence cellular imaging of internal organs in small animals,” Nature Protocols, Vol.7, No.8, pp.1456-1469, Aug. 2012. (Featured as the Journal Cover)
- “In vivo imaging of tracheal epithelial cells in mice during airway regeneration,” American Journal of Respiratory Cell and Molecular Biology(AJRCMB), Vol. 47, No.6, pp.864-868, Dec. 2012. (Most-read Article during Oct. 2012)

Cover article of
Journal of Biophotonics

Cover article of
Theranostics

Cover article of
Int. J. Med. Sci
